- Home
- Bookkeeping 101
- Profit and Loss Statement
Profit and Loss Statement
Do You Know How to Read Your P&L Report?
The Profit and Loss Statement can tell you a lot about how a business is doing. It can also help you to determine ways that you can go about saving money (so that there is more to bring home!)
Do you know how to read your financial statements? How about the other important statements show on my Bookkeeping 101 page?
A good many new business owners who are just getting started in their own business don't know how to read the two main financial statements. They are treating their money like it's a game.
Your business might not be operating for long if you don't learn to read and use the profit & loss statement and balance sheet.
It's a good thing you are already here to learn everything you need to know! ;)
Bookkeeping 101 E-Book
This Bookkeeping 101 EBook is a useful tool for business owners, bookkeepers, accountants and anyone responsible for household personal finances.
You can receive the complete Bookkeeping 101 accounting series in a 23 page E-Book for $4.97 along with all sorts of other accounting, business and financial goodies.
Profit and Loss Statement
A profit and loss statement, also known as an income statement or statement of earnings, is a financial statement that provides a summary of a company's revenues, expenses, gains, and losses over a specific period of time, typically on a quarterly or annual basis. It is an essential tool for assessing a company's financial performance and determining its profitability.
The profit and loss statement starts with the company's total revenue, which includes sales, fees, and any other income generated from its core operations. From this revenue, the statement deducts the cost of goods sold (COGS) or the direct expenses directly associated with producing or delivering the company's products or services. The resulting figure is known as the gross profit.
After calculating the gross profit, the statement further deducts operating expenses, such as salaries, rent, utilities, marketing costs, and other general administrative expenses. These expenses are necessary for running the day-to-day operations of the business. The difference between the gross profit and operating expenses is called the operating profit or operating income.
Next, the statement may include non-operating income or expenses, which are gains or losses from activities not directly related to the core operations of the business. Examples of non-operating items include interest income, interest expense, gains or losses from investments, and other miscellaneous income or expenses.
After accounting for non-operating items, the profit and loss statement arrive at the net profit before tax, which represents the company's profit or loss from its regular operations before accounting for taxes. Finally, taxes are deducted to calculate the net profit after tax, which represents the company's bottom line, or the amount of profit or loss generated after all expenses and taxes.
The profit and loss statement provides valuable insights into a company's financial health and performance. It helps stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and management, assess the company's ability to generate profit, control expenses, and manage its operations efficiently. By analyzing trends in revenues, expenses, and profitability over time, stakeholders can make informed decisions about the company's financial future.
Two Main Financial Statements
The two main financial statements are very useful in many ways.
One beneficial thing a profit and loss statement can do is to compare the current year's income and expenses to those of the previous year. This would indicate if the decisions you are making are helping you to make more money or less money.
The balance sheet in contrast gives you a view of your overall financial health and is an indication of whether your business is improving or going downhill.
The bookkeeping 101 financial statements can also be used by other people in ways that can benefit you or be to your detriment. An example of this would be when you are presenting your bookkeeping reports to a bank. The banker will look at these financial statements and try to predict how long he or she expects you to stay in business.
The profit & loss statement will basically tell the bank if your business is profitable or not. While the balance sheet will tell the bank how stable you are financially.
What you would typically want to see on a profit & loss statement would be a steady amount of growth in revenue and net income.
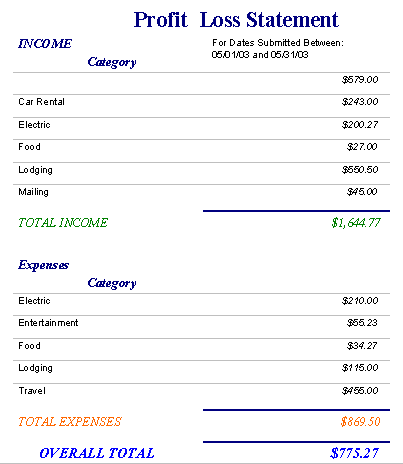
Sample Profit and Loss Statement
A sample profit and loss report might look something like this...
Reviewing a P&L Statement
After a company does a review of it's profit and loss statement, it might end up choosing not to grow in order to be able to increase their net income.
They might also decide to cut back on jobs that aren't making them as much money, or decide not to sell the types of products that are making them less money.
The Profit & Loss Statement is great to review in order to make sure that you are making money and not overspending on job costs or overhead expenses.
In contrast, on the balance sheet you would be looking for a higher amount of assets, a lower amount of liabilities, or a proportional amount of growth in assets over the liabilities.
An overall common rule of thumb is to try and keep the value of your assets at equal or at least two times the value of your liabilities. So if you have $200,000 in assets, you should have $100,000 or less in liabilities.
This would let you know that you are doing well and are right on track for the success that you seek!
I started this labor of love in 2008.
Thank you for making it one of the top visited sites about bookkeeping.
And thank you to "SBI!," which made it possible.
When you are in need of a bookkeeper, give me a call! Until then, I'd love to hear from you right here.
Bookkeeping 101 Articles
- Accounts Payable
- Accounts Receivable
- Balance Sheet
- Bank Reconciliation
- Chart of Accounts
- Profit and Loss Statement
Please subscribe to my monthly newsletter, Bookkeeping Basics E-zine. It tells you every month about the new information that I have added, including some great tips and advice from myself and other Bookkeeping Basics readers.
Like Bookkeeping-Basics.net?
- Home
- Bookkeeping 101
- Profit and Loss Statement

















New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.